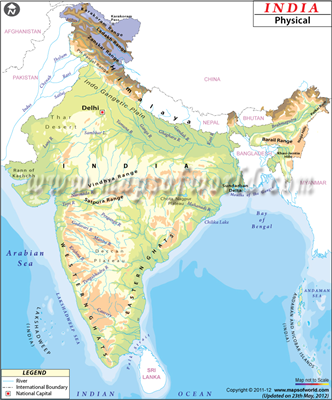
India is home to one of the most diverse mountain systems of the world.
The Aravallis are the oldest mountain ranges of the world, whereas the
Himalayas are the youngest fold mountains. Indian mountain system can mainly be
divided into following categories :
1.
The Himalayas
2.
The Trans – Himalayas
3.
The Central Highlands
4.
The Peninsular Mountains
The Himalaya : Northern
Mountains
The Himalayas
in India Means 'Abode of Snow'. They are one of the youngest fold mountain ranges
in the world and comprise mainly sedimentary rocks. They stretch from the Indus
River in the west to the Brahmaputra River in the east. Total length is about
5000 km. The width of the Himalayas varies from 500 km in Kashmir to 200 km in
Arunachal Pradesh. Their average height is 2000m. The Eastern Himalayas-made up
of Patkai Hills, Naga Hills, Mizo Hills and the Garo, Khasi and Jaintia
Hills-are also known as Purvanchal.
The Pamir, popularly known as the Roof of the World, is the connecting
link between the Himalayas and the high ranges of Central Asia. The Himalayas can
be divided into 3 parallel or longitudinal zones, each with separate features.
The Greater Himalayas or The Himadri : Average elevation (height above the sea level) extends up to 6000m & they
are home to some of the world's highest peaks. Following are the main peaks (with
their heights & location) of this region.
 Mt Everest (or Sagarmatha or Chomo Langma) - 8850 m (in Nepal)
Mt Everest (or Sagarmatha or Chomo Langma) - 8850 m (in Nepal)
 Mt Kanchenjunqa - 8598 m (in India)
Mt Kanchenjunqa - 8598 m (in India)
 Mt Makalu - 8481 m (in Nepal)
Mt Makalu - 8481 m (in Nepal)
 Mt Dhaulaqiri - 8172 m (in Nepal)
Mt Dhaulaqiri - 8172 m (in Nepal)
 Mt Cho Oyu - 8153m (in Nepal)
Mt Cho Oyu - 8153m (in Nepal)
 Mt Nanga Parbat - 8126m (in India)
Mt Nanga Parbat - 8126m (in India)
 Mt Annapurna - 8078 m (in Nepal)
Mt Annapurna - 8078 m (in Nepal)
 Mt Nando Devi - 7817 m (in
India)
Mt Nando Devi - 7817 m (in
India)
There are many passes and most of them have a height above 4,500 m. Main
passes are Shipki La and Bara Lapcha La in Himachal Pradesh, Burzil and Zozi La
in Kashmir, Niti, Lipulekh and Thag La in Uttarankhand, and Jelep La and Nathu
La in Sikkim.
Lesser Himalayas or The Himachal :
 Average height of mountains is 3700 - 4500 m.
Average height of mountains is 3700 - 4500 m.
 Mountains and valleys are disposed in all direction (mountains rising to
5000 m and the valleys touching 1000 m).
Mountains and valleys are disposed in all direction (mountains rising to
5000 m and the valleys touching 1000 m).
 Its important
ranges are : Dhauladhar, Pir Panjal, Nag Tibba, Mussoorie.
Its important
ranges are : Dhauladhar, Pir Panjal, Nag Tibba, Mussoorie.
 Important hill
resorts are : Shimla, Chhail, Ranikhet, Chakrata, Mussoorie, Nainital, Almora,
Darjeeling.
Important hill
resorts are : Shimla, Chhail, Ranikhet, Chakrata, Mussoorie, Nainital, Almora,
Darjeeling.
Outer Himalayas or The Shiwaliks :
 Lowest range (average elevation is 900-1200 m).
Lowest range (average elevation is 900-1200 m).
 Forms the foothills and lies between the Lesser Himalayas and the plains.
It is the newest range.
Forms the foothills and lies between the Lesser Himalayas and the plains.
It is the newest range.
Trans - Himalayan Zone
 This range lies to the north of the Great Himalayas. It has some important
ranges like Karakoram, Laddakh, Zanskar, etc. the highest peak in this region
is K2 or Godwin Austin (8611m, in Pak occupied Kashmir). Other high peaks are
Hidden Peak (8068 m), Broad Peak (8047 m) and Gasherbrum II (8035 m).
This range lies to the north of the Great Himalayas. It has some important
ranges like Karakoram, Laddakh, Zanskar, etc. the highest peak in this region
is K2 or Godwin Austin (8611m, in Pak occupied Kashmir). Other high peaks are
Hidden Peak (8068 m), Broad Peak (8047 m) and Gasherbrum II (8035 m).
 The longest glacier is Siachin in the Nubra valley, which is more than 72
km long (biggest glacier in the world). Biafo, Baltaro, Batura, Hispar are the
other important glaciers in this region.
The longest glacier is Siachin in the Nubra valley, which is more than 72
km long (biggest glacier in the world). Biafo, Baltaro, Batura, Hispar are the
other important glaciers in this region.
 This area is the largest snow-field outside the Polar Regions.
This area is the largest snow-field outside the Polar Regions.
Peninsular Mountains
 While the Himalayas are Fold Mountains, they are not.
While the Himalayas are Fold Mountains, they are not.
 The Aravalli
Mountains (Rajasthan) : World's oldest. Guru Shikhar is the highest peak on which Mount Abu (1,722
m) is situated.
The Aravalli
Mountains (Rajasthan) : World's oldest. Guru Shikhar is the highest peak on which Mount Abu (1,722
m) is situated.
 The Vindhya Mountains
The Vindhya Mountains
 The Satpura Mountains (highest point at Dhupgarh [1,350 m] near Pachmarhi)
The Satpura Mountains (highest point at Dhupgarh [1,350 m] near Pachmarhi)
 The Western
Ghats or Sahyadris : Average height 1200mtrs, 1600km long. Its southern part is separated
from the main Sahyadri range by Palghat Gap (link between Tamil Nadu &
Kerala). Other passes are Thalghat (connects Nasik to Mumbai) and Bhorghat
(connects Pune to Mumbai).
The Western
Ghats or Sahyadris : Average height 1200mtrs, 1600km long. Its southern part is separated
from the main Sahyadri range by Palghat Gap (link between Tamil Nadu &
Kerala). Other passes are Thalghat (connects Nasik to Mumbai) and Bhorghat
(connects Pune to Mumbai).
 The Eastern Ghats (Highest peak : Mahendra Giri
(1501 m)).
The Eastern Ghats (Highest peak : Mahendra Giri
(1501 m)).
 The Nilgiris
or The Blue Mountains : Meeting place of the Western and the Eastern Ghats. Two highest peaks are
Dodda Betta and Makurti.
The Nilgiris
or The Blue Mountains : Meeting place of the Western and the Eastern Ghats. Two highest peaks are
Dodda Betta and Makurti.
 The highest peak of Peninsular India is Anaimudi (2695 m) in Anaimalai Hills.
The highest peak of Peninsular India is Anaimudi (2695 m) in Anaimalai Hills.
Cardamom hills or
Ealaimalai is the southernmost mountain range of India.